- Research Briefing
- Published:
Subjects
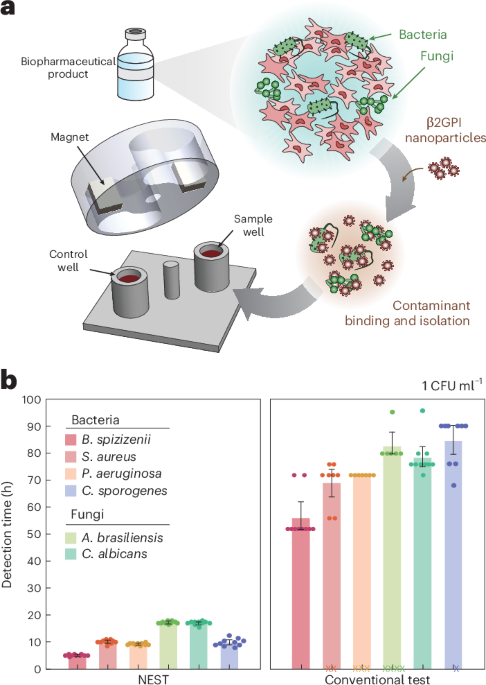
A synthetic peptide nanoparticle and microfluidic chip enable sterility testing of cell- and gene-based therapeutics in under 18 hours, bridging a long-standing safety gap for biopharmaceutical products that cannot undergo terminal sterilization and have limited shelf life.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
$32.99 / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $9.92 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

References
-
Rader, R. A. (Re)defining biopharmaceutical. Nat. Biotechnol. 26, 743–751 (2008). An article that defines the scope of biopharmaceuticals and their distinction from conventional, chemically synthesized drugs.
-
Baker, D. J. et al. CAR T therapy beyond cancer: the evolution of a living drug. Nature 619, 707–715 (2023). An article presenting CAR T cells as a living therapeutic that eradicates refractory blood cancers and might also extend to non-cancer diseases.
-
Cundell, T., Atkins, J. W. & Lau, A. F. Sterility testing for hematopoietic stem cells. J. Clin. Microbiol. 61, e0165422 (2023). An article that reviews current sterility testing practices for haematopoietic stem cells and discusses strategies to enhance speed and safety in clinical applications.
-
Kim, T. H. et al. Blood culture-free ultra-rapid antimicrobial susceptibility testing. Nature 632, 893–902 (2024). An article that presents a synthetic-peptide nanoparticle for rapid microbial detection in clinical diagnostics.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This is a summary of: Kang, J. et al. One-day rapid sterility test for human-derived biopharmaceuticals. Nat. Biomed. Eng. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41551-025-01524-3 (2025).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Accelerated sterility testing unlocks safe delivery of life-saving therapies. Nat. Biomed. Eng (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41551-025-01557-8
-
Published:
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41551-025-01557-8