Iuchi, S. et al. Regulation of drought tolerance by gene manipulation of 9-cis-epoxycarotenoid dioxygenase, a key enzyme in abscisic acid biosynthesis in Arabidopsis. Plant J. 27, 325–333 (2001).
Hancock, J. F. A framework for assessing the risk of transgenic Crops. Bioscience 53, 512–519 (2003).
He, R. et al. Overexpression of 9-cis-epoxycarotenoid dioxygenase cisgene in grapevine increases drought tolerance and results in pleiotropic effects. Front. Plant Sci. 9, 970 (2018).
Khan, M. A. et al. CRISPRi-based circuits to control gene expression in plants. Nat. Biotechnol. 43, 416–430 (2024).
Brophy, J. A. N. et al. Synthetic genetic circuits as a means of reprogramming plant roots. Science 377, 747–751 (2022).
Lloyd, J. P. B. et al. Synthetic memory circuits for stable cell reprogramming in plants. Nat. Biotechnol. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41587-022-01383-2 (2022).
Khan, A. & Lister, R. Synthetic gene circuits in plants: recent advances and challenges. Quant. Plant Biol. 6, e6 (2025).
Lloyd, J. P. B., Khan, A. & Lister, R. The switch-liker’s guide to plant synthetic gene circuits. Plant J. 121, e70090 (2025).
Brophy, J. A. N. & Voigt, C. A. Principles of genetic circuit design. Nat. Methods 11, 508–520 (2014).
Kiani, S. et al. CRISPR transcriptional repression devices and layered circuits in mammalian cells. Nat. Methods 11, 723–726 (2014).
Gander, M. W., Vrana, J. D., Voje, W. E., Carothers, J. M. & Klavins, E. Digital logic circuits in yeast with CRISPR–dCas9 NOR gates. Nat. Commun. 8, 15459 (2017).
Vazquez-Vilar, M., Selma, S. & Orzaez, D. The design of synthetic gene circuits in plants: new components, old challenges. J. Exp. Bot. 74, 3791–380 (2023).
Wang, Y. & Demirer, G. S. Synthetic biology for plant genetic engineering and molecular farming. Trends Biotechnol. 41, 1182–1198 (2023).
Gaber, R. et al. Designable DNA-binding domains enable construction of logic circuits in mammalian cells. Nat. Chem. Biol. 10, 203–208 (2014).
Weinberg, B. H. et al. Large-scale design of robust genetic circuits with multiple inputs and outputs for mammalian cells. Nat. Biotechnol. 35, 453–462 (2017).
Santos-Moreno, J., Tasiudi, E., Stelling, J. & Schaerli, Y. Multistable and dynamic CRISPRi-based synthetic circuits. Nat. Commun. 11, 2746 (2020).
Kar, S. et al. Orthogonal control of gene expression in plants using synthetic promoters and CRISPR-based transcription factors. Plant Methods 18, 42 (2022).
Guiziou, S., Maranas, C. J., Chu, J. C. & Nemhauser, J. L. An integrase toolbox to record gene-expression during plant development. Nat. Commun. 14, 1844 (2023).
Schaumberg, K. A. et al. Quantitative characterization of genetic parts and circuits for plant synthetic biology. Nat. Methods 13, 94 (2015).
Ming, M. et al. CRISPR–Cas12b enables efficient plant genome engineering. Nat. Plants 6, 202–208 (2020).
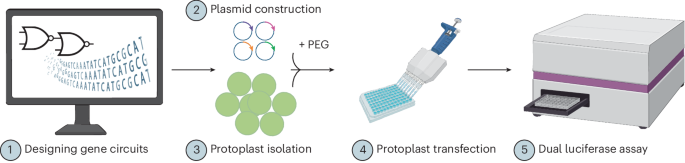
Fujikawa, Y. et al. Split luciferase complementation assay to detect regulated protein-protein interactions in rice protoplasts in a large-scale format. Rice 7, 11 (2014).
Rigoulot, S. B. et al. Automated, high-throughput protoplast transfection for gene editing and transgene expression studies. Methods Mol. Biol. 2653, 129–149 (2023).
Moreno-Giménez, E., Selma, S., Calvache, C. & Orzáez, D. GB_SynP: a modular dCas9-regulated synthetic promoter collection for fine-tuned recombinant gene expression in plants. ACS Synth. Biol. 11, 3037–3048 (2022).
Calvache, C., Vazquez-Vilar, M., Moreno-Giménez, E. & Orzaez, D. A quantitative autonomous bioluminescence reporter system with a wide dynamic range for plant synthetic biology. Plant Biotechnol. J. 22, 37–47 (2024).
Rademacher, T. et al. Plant cell packs: a scalable platform for recombinant protein production and metabolic engineering. Plant Biotechnol. J. 17, 1560–1566 (2019).
Jusiak, B. et al. Synthetic gene circuits. In Encyclopedia of Molecular Cell Biology and Molecular Medicine Vol. 4 (ed. Meyers, R. A.) 1–56 (Wiley–VCH, 2014).
Jusiak, B., Cleto, S., Perez-Piñera, P. & Lu, T. K. Engineering synthetic gene circuits in living cells with CRISPR technology. Trends Biotechnol. 34, 535–547 (2016).
Haurwitz, R. E., Jinek, M., Wiedenheft, B., Zhou, K. & Doudna, J. A. Sequence- and structure-specific RNA processing by a CRISPR endonuclease. Science 329, 1355–1358 (2010).
Goodstein, D. M. et al. Phytozome: a comparative platform for green plant genomics. Nucleic Acids Res. 40, D1178–D1186 (2012).
Shahmuradov, I. A., Umarov, R. K. & Solovyev, V. V. TSSPlant: a new tool for prediction of plant Pol II promoters. Nucleic Acids Res. 45, e65 (2017).
Lai, H.-Y. et al. IProEP: a computational predictor for predicting promoter. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 17, 337–346 (2019).
Umarov, R., Kuwahara, H., Li, Y., Gao, X. & Solovyev, V. Promoter analysis and prediction in the human genome using sequence-based deep learning models. Bioinformatics 35, 2730–2737 (2019).
Gibson, D. G. et al. Enzymatic assembly of DNA molecules up to several hundred kilobases. Nat. Methods 6, 343–345 (2009).
Engler, C. et al. A golden gate modular cloning toolbox for plants. ACS Synth. Biol. 3, 839–843 (2014).
Cove, D. J. et al. The moss Physcomitrella patens: a novel model system for plant development and genomic studies. Cold Spring Harb. Protoc. 2009, db.emo115 (2009).
Khan, M. A. et al. CRISPRi-based circuits to control gene expression in plants. Zenodo https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.11108565 (2024).
Swain, T. et al. A modular dCas9-based recruitment platform for combinatorial epigenome editing. Nucleic Acids Res. 52, 474–491 (2024).
Cano-Rodriguez, D. et al. Writing of H3K4Me3 overcomes epigenetic silencing in a sustained but context-dependent manner. Nat. Commun. 7, 12284 (2016).
Konermann, S. et al. Transcriptome engineering with RNA-targeting type VI-D CRISPR effectors. Cell 173, 665–676.e14 (2018).
Garcia-Bloj, B. et al. Waking up dormant tumor suppressor genes with zinc fingers, TALEs and the CRISPR–dCas9 system. Oncotarget 7, 60535–60554 (2016).
Shechner, D. M., Hacisuleyman, E., Younger, S. T. & Rinn, J. L. Multiplexable, locus-specific targeting of long RNAs with CRISPR-Display. Nat. Methods 12, 664–670 (2015).
Amabile, A. et al. Inheritable silencing of endogenous genes by hit-and-run targeted epigenetic editing. Cell 167, 219–232.e14 (2016).
Gilbert, L. A. et al. CRISPR-mediated modular RNA-guided regulation of transcription in eukaryotes. Cell 154, 442–451 (2013).
Maeder, M. L. et al. CRISPR RNA-guided activation of endogenous human genes. Nat. Methods 10, 977–979 (2013).
Qi, L. S. et al. Repurposing CRISPR as an RNA-guided platform for sequence-specific control of gene expression. Cell 152, 1173–1183 (2013).
Bikard, D. et al. Programmable repression and activation of bacterial gene expression using an engineered CRISPR-Cas system. Nucleic Acids Res. 41, 7429–7437 (2013).
Ohta, M., Matsui, K., Hiratsu, K., Shinshi, H. & Ohme-Takagi, M. Repression domains of class II ERF transcriptional repressors share an essential motif for active repression. Plant Cell 13, 1959–1968 (2001).
Hiratsu, K., Matsui, K., Koyama, T. & Ohme-Takagi, M. Dominant repression of target genes by chimeric repressors that include the EAR motif, a repression domain, in Arabidopsis. Plant J. 34, 733–739 (2003).
Liu, H. et al. CRISPR-P 2.0: an improved CRISPR–Cas9 tool for genome editing in plants. Mol. Plant 10, 530–532 (2017).
Xie, X. et al. CRISPR-GE: a convenient software toolkit for CRISPR-based genome editing. Mol. Plant 10, 1246–1249 (2017).
Park, J., Bae, S. & Kim, J.-S. Cas-Designer: a web-based tool for choice of CRISPR–Cas9 target sites. Bioinformatics 31, 4014–4016 (2015).
Tian, F., Yang, D.-C., Meng, Y.-Q., Jin, J. & Gao, G. PlantRegMap: charting functional regulatory maps in plants. Nucleic Acids Res. 48, D1104–D1113 (2020).
Fornes, O. et al. JASPAR 2020: update of the open-access database of transcription factor binding profiles. Nucleic Acids Res. 48, D87–D92 (2020).
Chow, C.-N. et al. PlantPAN3.0: a new and updated resource for reconstructing transcriptional regulatory networks from ChIP-seq experiments in plants. Nucleic Acids Res. 47, D1155–D1163 (2019).
Bae, S., Park, J. & Kim, J.-S. Cas-OFFinder: a fast and versatile algorithm that searches for potential off-target sites of Cas9 RNA-guided endonucleases. Bioinformatics 30, 1473–1475 (2014).