- Tools of the Trade
- Published:
Subjects
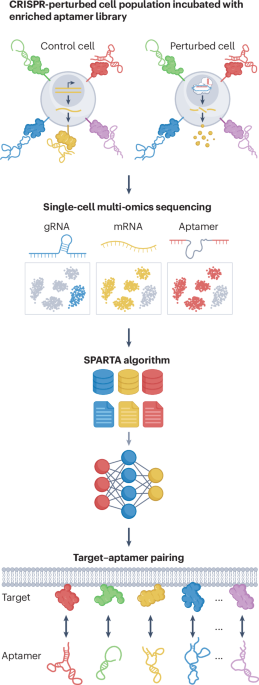
Cell-surface proteins serve as the primary gateway for intercellular communication and account for over 60% of current therapeutic targets. Despite this clinical importance, the development of high-affinity molecular probes, such as aptamers, that target cell-surface proteins is a substantial bottleneck in precision medicine. Although Cell-SELEX (systematic evolution of ligands by exponential enrichment) enables the selection of aptamers within native cellular environments, identifying their precise molecular targets has remained a low-throughput and resource-intensive ‘black box’. This issue is now being addressed by the emerging field of ‘aptomics’, defined here as the high-throughput, systematic study of the entire aptamer interaction landscape, integrating large-scale sequence diversity with comprehensive target identification and kinetics characterization.
SPARK-seq has notable advantages over traditional mass spectrometry-based identification of aptamer–ligand pairs. It achieves nanomolar level sensitivity and unparalleled specificity because cells with distinct genetic perturbations serve as mutual internal controls to filter out nonspecific background noise. Indeed, we demonstrated that SPARK-seq was able to precisely discriminate targets with high structural homology, such as NRP1 and NRP2, while maintaining robust performance across protein expression levels spanning several orders of magnitude. Furthermore, SPARK-seq prioritizes stably bound aptamers (that is, those with slow dissociation rates), which is an essential feature for therapeutic and diagnostic applications.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
$32.99 / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

References
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The author declares no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, Q. High-throughput identification of aptamer–target pairs with SPARK-seq. Nat Rev Genet (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41576-026-00938-2
-
Published:
-
Version of record:
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41576-026-00938-2