Anderson, D. G., Lynn, D. M. & Langer, R. Semi-automated synthesis and screening of a large library of degradable cationic polymers for gene delivery. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 42, 3153–3158 (2003).
Breunig, M., Lungwitz, U., Liebl, R. & Goepferich, A. Breaking up the correlation between efficacy and toxicity for nonviral gene delivery. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 104, 14454–14459 (2007).
Lynn, D. M. & Langer, R. Degradable poly(β-amino esters): synthesis, characterization, and self-assembly with plasmid DNA. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 122, 10761–10768 (2000).
Siegwart, D. J. et al. Combinatorial synthesis of chemically diverse core-shell nanoparticles for intracellular delivery. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 108, 12996–13001 (2011).
Wightman, L. et al. Different behavior of branched and linear polyethylenimine for gene delivery in vitro and in vivo. J. Gene Med. 3, 362–372 (2001).
Dahlman, J. E. et al. In vivo endothelial siRNA delivery using polymeric nanoparticles with low molecular weight. Nat. Nanotechnol. 9, 648–655 (2014).
Patra, J. K. et al. Nano based drug delivery systems: recent developments and future prospects. J. Nanobiotechnol. 16, 71 (2018).
Anselmo, A. C. & Mitragotri, S. Nanoparticles in the clinic: an update. Bioeng. Transl. Med. 4, e10143 (2019).
Maurer, M. S. et al. Patisiran treatment in patients with transthyretin cardiac amyloidosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 389, 1553–1565 (2023).
Hassett, K. J. et al. Optimization of lipid nanoparticles for intramuscular administration of mRNA vaccines. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 15, 1–11 (2019).
Verma, M. et al. The landscape for lipid-nanoparticle-based genomic medicines. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 22, 349–350 (2023).
Dehghani-Ghahnaviyeh, S. et al. Ionizable amino lipids distribution and effects on DSPC/cholesterol membranes: implications for lipid nanoparticle structure. J. Phys. Chem. B 127, 6928–6939 (2023).
McDonald, S. M. et al. Applied machine learning as a driver for polymeric biomaterials design. Nat. Commun. 14, 4838 (2023).
Li, B. et al. Accelerating ionizable lipid discovery for mRNA delivery using machine learning and combinatorial chemistry. Nat. Mater. 23, 1002–1008 (2024).
Han, X. et al. Fast and facile synthesis of amidine-incorporated degradable lipids for versatile mRNA delivery in vivo. Nat. Chem. 16, 1687–1697 (2024).
Han, X. et al. Optimization of the activity and biodegradability of ionizable lipids for mRNA delivery via directed chemical evolution. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 8, 1412–1424 (2024).
Xue, L. et al. Combinatorial design of siloxane-incorporated lipid nanoparticles augments intracellular processing for tissue-specific mRNA therapeutic delivery. Nat. Nanotechnol. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41565-024-01747-6 (2024).
Han, X. et al. Adjuvant lipidoid-substituted lipid nanoparticles augment the immunogenicity of SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccines. Nat. Nanotechnol. 18, 1105–1114 (2023).
Han, X. et al. An ionizable lipid toolbox for RNA delivery. Nat. Commun. 12, 7233 (2021).
Cheng, Q. et al. Selective organ targeting (SORT) nanoparticles for tissue-specific mRNA delivery and CRISPR–Cas gene editing. Nat. Nanotechnol. 15, 313–320 (2020).
Dilliard, S. A. & Siegwart, D. J. Passive, active and endogenous organ-targeted lipid and polymer nanoparticles for delivery of genetic drugs. Nat. Rev. Mater. 8, 282–300 (2023).
Mitchell, M. J. et al. Engineering precision nanoparticles for drug delivery. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 20, 101–124 (2021).
Billingsley, M. M. et al. Orthogonal design of experiments for optimization of lipid nanoparticles for mRNA engineering of CAR T cells. Nano Lett. 22, 533–542 (2022).
Lokugamage, M. P. et al. Optimization of lipid nanoparticles for the delivery of nebulized therapeutic mRNA to the lungs. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 5, 1059–1068 (2021).
Hou, X., Zaks, T., Langer, R. & Dong, Y. Lipid nanoparticles for mRNA delivery. Nat. Rev. Mater. 6, 1078–1094 (2021).
Patel, S. et al. Naturally-occurring cholesterol analogues in lipid nanoparticles induce polymorphic shape and enhance intracellular delivery of mRNA. Nat. Commun. 11, 983 (2020).
Lokugamage, M. P., Sago, C. D. & Dahlman, J. E. Testing thousands of nanoparticles in vivo using DNA barcodes. Curr. Opin. Biomed. Eng. 7, 1–8 (2018).
Zheng, L., Bandara, S. R., Tan, Z. & Leal, C. Lipid nanoparticle topology regulates endosomal escape and delivery of RNA to the cytoplasm. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 120, e2301067120 (2023).
Koltover, I., Salditt, T., Rädler, J. O. & Safinya, C. R. An inverted hexagonal phase of cationic liposome-DNA complexes related to DNA release and delivery. Science 281, 78–81 (1998).
Álvarez-Benedicto, E. et al. Optimization of phospholipid chemistry for improved lipid nanoparticle (LNP) delivery of messenger RNA (mRNA). Biomater. Sci. 10, 549–559 (2022).
Herrera, M., Kim, J., Eygeris, Y., Jozic, A. & Sahay, G. Illuminating endosomal escape of polymorphic lipid nanoparticles that boost mRNA delivery. Biomater. Sci. 9, 4289–4300 (2021).
Radmand, A. et al. Cationic cholesterol-dependent LNP delivery to lung stem cells, the liver, and heart. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 121, e2307801120 (2024).
Mui, B. L. et al. Influence of polyethylene glycol lipid desorption rates on pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of siRNA lipid nanoparticles. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2, e139 (2013).
Gindy, M. E. et al. Mechanism of macromolecular structure evolution in self-assembled lipid nanoparticles for siRNA delivery. Langmuir 30, 4613–4622 (2014).
Kauffman, K. J. et al. Optimization of lipid nanoparticle formulations for mRNA delivery in vivo with fractional factorial and definitive screening designs. Nano Lett. 15, 7300–7306 (2015).
Akinc, A. et al. A combinatorial library of lipid-like materials for delivery of RNAi therapeutics. Nat. Biotechnol. 26, 561–569 (2008).
Billingsley, M. M. et al. Ionizable lipid nanoparticle-mediated mRNA delivery for human CAR T cell engineering. Nano Lett. 20, 1578–1589 (2020).
Whitehead, K. A. et al. Degradable lipid nanoparticles with predictable in vivo siRNA delivery activity. Nat. Commun. 5, 4277 (2014).
Hajj, K. A. et al. Branched-tail lipid nanoparticles potently deliver mRNA in vivo due to enhanced ionization at endosomal pH. Small 15, 1805097 (2019).
Yonezawa, S., Koide, H. & Asai, T. Recent advances in siRNA delivery mediated by lipid-based nanoparticles. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 154, 64–78 (2020).
Li, H. et al. Circular RNA cancer vaccines drive immunity in hard-to-treat malignancies. Theranostics 12, 6422–6436 (2022).
McKay, P. F. et al. Self-amplifying RNA SARS-CoV-2 lipid nanoparticle vaccine candidate induces high neutralizing antibody titers in mice. Nat. Commun. 11, 3523 (2020).
Palanki, R. et al. Ionizable lipid nanoparticles for therapeutic base editing of congenital brain disease. ACS Nano 17, 13594–13610 (2023).
Wei, T. et al. Lung SORT LNPs enable precise homology-directed repair mediated CRISPR/Cas genome correction in cystic fibrosis models. Nat. Commun. 14, 7322 (2023).
Thatte, A. S. et al. mRNA lipid nanoparticles for ex vivo engineering of immunosuppressive T cells for autoimmunity therapies. Nano Lett. 23, 10179–10188 (2023).
Billingsley, M. M. et al. In vivo mRNA CAR T cell engineering via targeted ionizable lipid nanoparticles with extrahepatic tropism. Small 20, 2304378 (2024).
Love, K. T. et al. Lipid-like materials for low-dose, in vivo gene silencing. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 107, 1864–1869 (2010).
Forsyth, V., Rzeczycki, P., Taylor, D. & Ariosa, A. Enhancing transfection efficiency of primary immune cells through lipid nanoparticle mediated delivery. J. Immunol. 212, 0857_6526 (2024).
Dilliard, S. A., Cheng, Q. & Siegwart, D. J. On the mechanism of tissue-specific mRNA delivery by selective organ targeting nanoparticles. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 118, e2109256118 (2021).
Sun, Y. et al. In vivo editing of lung stem cells for durable gene correction in mice. Science 384, 1196–1202 (2024).
Qiu, M. et al. Lung-selective mRNA delivery of synthetic lipid nanoparticles for the treatment of pulmonary lymphangioleiomyomatosis. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 119, e2116271119 (2022).
LoPresti, S. T., Arral, M. L., Chaudhary, N. & Whitehead, K. A. The replacement of helper lipids with charged alternatives in lipid nanoparticles facilitates targeted mRNA delivery to the spleen and lungs. J. Control. Release 345, 819–831 (2022).
Omo-Lamai, S. et al. Physicochemical targeting of lipid nanoparticles to the lungs induces clotting: mechanisms and solutions. Adv. Mater. 36, 2312026 (2024).
Walkey, C. D. et al. Protein corona fingerprinting predicts the cellular interaction of gold and silver nanoparticles. ACS Nano 8, 2439–2455 (2014).
Walkey, C. D., Olsen, J. B., Guo, H., Emili, A. & Chan, W. C. W. Nanoparticle size and surface chemistry determine serum protein adsorption and macrophage uptake. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 134, 2139–2147 (2012).
Cai, R. et al. Dynamic intracellular exchange of nanomaterials’ protein corona perturbs proteostasis and remodels cell metabolism. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 119, e2200363119 (2022).
Abdelkhaliq, A. et al. Impact of nanoparticle surface functionalization on the protein corona and cellular adhesion, uptake and transport. J. Nanobiotechnol. 16, 70 (2018).
Baimanov, D. et al. In situ analysis of nanoparticle soft corona and dynamic evolution. Nat. Commun. 13, 5389 (2022).
Lee, Y. K., Choi, E.-J., Webster, T. J., Kim, S.-H. & Khang, D. Effect of the protein corona on nanoparticles for modulating cytotoxicity and immunotoxicity. Int. J. Nanomed. 10, 97–113 (2015).
Mahmoudi, M., Landry, M. P., Moore, A. & Coreas, R. The protein corona from nanomedicine to environmental science. Nat. Rev. Mater. 8, 422–438 (2023).
Xu, Y. et al. AGILE platform: a deep learning powered approach to accelerate LNP development for mRNA delivery. Nat. Commun. 15, 6305 (2024).
Cheng, L. et al. Machine learning elucidates design features of plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid lipid nanoparticles for cell type-preferential transfection. ACS Nano 18, 28735–28747 (2024).
Dormán, G. The rise, fall and revival of combinatorial chemistry. Nachr. Chem. 70, 70–72 (2022).
Liu, Y. et al. Ultrastiff metamaterials generated through a multilayer strategy and topology optimization. Nat. Commun. 15, 2984 (2024).
Ha, C. S. et al. Rapid inverse design of metamaterials based on prescribed mechanical behavior through machine learning. Nat. Commun. 14, 5765 (2023).
Coley, C. W. et al. A robotic platform for flow synthesis of organic compounds informed by AI planning. Science 365, eaax1566 (2019).
Hashiba, K. et al. Branching ionizable lipids can enhance the stability, fusogenicity, and functional delivery of mRNA. Small Sci. 3, 2200071 (2023).
Mukalel, A. J. et al. Oxidized mRNA lipid nanoparticles for in situ chimeric antigen receptor monocyte engineering. Adv. Funct. Mater. 34, 2312038 (2024).
Riley, R. S. et al. Ionizable lipid nanoparticles for in utero mRNA delivery. Sci. Adv. 7, eaba1028 (2021).
Chen, J. et al. Combinatorial design of ionizable lipid nanoparticles for muscle-selective mRNA delivery with minimized off-target effects. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 120, e2309472120 (2023).
Fenton, O. S. et al. Synthesis and biological evaluation of ionizable lipid materials for the in vivo delivery of messenger RNA to B lymphocytes. Adv. Mater. 29, 1606944 (2017).
Fenton, O. S. et al. Bioinspired alkenyl amino alcohol ionizable lipid materials for highly potent in vivo mRNA delivery. Adv. Mater. 28, 2939–2943 (2016).
Hatit, M. Z. C. et al. Nanoparticle stereochemistry-dependent endocytic processing improves in vivo mRNA delivery. Nat. Chem. 15, 508–515 (2023).
Da Silva Sanchez, A. J. et al. Substituting racemic ionizable lipids with stereopure ionizable lipids can increase mRNA delivery. J. Control. Release 353, 270–277 (2023).
Li, Z. et al. Enzyme-catalyzed one-step synthesis of ionizable cationic lipids for lipid nanoparticle-based mRNA COVID-19 vaccines. ACS Nano 16, 18936–18950 (2022).
Jacobsen, E. N. Asymmetric catalysis of epoxide ring-opening reactions. Acc. Chem. Res. 33, 421–431 (2000).
Li, B. et al. Combinatorial design of nanoparticles for pulmonary mRNA delivery and genome editing. Nat. Biotechnol. 41, 1410–1415 (2023).
Lee, J. et al. A fully automated platform for photoinitiated RAFT polymerization. Digit. Discov. 2, 219–233 (2023).
Götz, J. et al. High-throughput synthesis provides data for predicting molecular properties and reaction success. Sci. Adv. 9, eadj2314 (2023).
Kong, F., Yuan, L., Zheng, Y. F. & Chen, W. Automatic liquid handling for life science: a critical review of the current state of the art. SLAS Technol. 17, 169–185 (2012).
Burger, B. et al. A mobile robotic chemist. Nature 583, 237–241 (2020).
Dai, T. et al. Autonomous mobile robots for exploratory synthetic chemistry. Nature 635, 890–897 (2024).
Steiner, S. et al. Organic synthesis in a modular robotic system driven by a chemical programming language. Science 363, eaav2211 (2019).
Nambiar, A. M. K. et al. Bayesian optimization of computer-proposed multistep synthetic routes on an automated robotic flow platform. ACS Cent. Sci. 8, 825–836 (2022).
Shields, B. J. et al. Bayesian reaction optimization as a tool for chemical synthesis. Nature 590, 89–96 (2021).
Ahneman, D. T., Estrada, J. G., Lin, S., Dreher, S. D. & Doyle, A. G. Predicting reaction performance in C–N cross-coupling using machine learning. Science 360, 186–190 (2018).
Fromer, J. C. & Coley, C. W. An algorithmic framework for synthetic cost-aware decision making in molecular design. Nat. Comput. Sci. 4, 440–450 (2024).
Kyranos, J. N., Cai, H., Wei, D. & Goetzinger, W. K. High-throughput high-performance liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry for modern drug discovery. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 12, 105–111 (2001).
Ginsburg-Moraff, C. et al. Integrated and automated high-throughput purification of libraries on microscale. SLAS Technol. 27, 350–360 (2022).
Su, W.-C. et al. A platform method for simultaneous quantification of lipid and nucleic acid components in lipid nanoparticles. J. Chromatogr. A 1746, 465788 (2025).
Munjoma, N. et al. High throughput LC-MS platform for large scale screening of bioactive polar lipids in human plasma and serum. J. Proteome Res. 21, 2596–2608 (2022).
Haas, C. P. et al. Open-source chromatographic data analysis for reaction optimization and screening. ACS Cent. Sci. 9, 307–317 (2023).
Herck, J. V. et al. Operator-independent high-throughput polymerization screening based on automated inline NMR and online SEC. Digit. Discov. 1, 519–526 (2022).
Ammini, G. D., Hooker, J. P., Herck, J. V., Kumar, A. & Junkers, T. Comprehensive high-throughput screening of photopolymerization under light intensity variation using inline NMR monitoring. Polym. Chem. 14, 2708–2716 (2023).
Hu, G. & Qiu, M. Machine learning-assisted structure annotation of natural products based on MS and NMR data. Nat. Prod. Rep. 40, 1735–1753 (2023).
Kulkarni, J. A. et al. On the formation and morphology of lipid nanoparticles containing ionizable cationic lipids and siRNA. ACS Nano 12, 4787–4795 (2018).
Maeki, M. et al. Understanding the formation mechanism of lipid nanoparticles in microfluidic devices with chaotic micromixers. PLoS ONE 12, e0187962 (2017).
Jung, H. N., Lee, S.-Y., Lee, S., Youn, H. & Im, H.-J. Lipid nanoparticles for delivery of RNA therapeutics: current status and the role of in vivo imaging. Theranostics 12, 7509–7531 (2022).
Strelkova Petersen, D. M., Chaudhary, N., Arral, M. L., Weiss, R. M. & Whitehead, K. A. The mixing method used to formulate lipid nanoparticles affects mRNA delivery efficacy and organ tropism. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 192, 126–135 (2023).
Padilla, M. et al. Solution biophysics identifies lipid nanoparticle non-sphericity, polydispersity, and dependence on internal ordering for efficacious mRNA delivery. Preprint at bioRxiv https://doi.org/10.1101/2024.12.19.629496 (2025).
Fan, Y. et al. Automated high-throughput preparation and characterization of oligonucleotide-loaded lipid nanoparticles. Int. J. Pharm. 599, 120392 (2021).
Valente, I., Celasco, E., Marchisio, D. L. & Barresi, A. A. Nanoprecipitation in confined impinging jets mixers: production, characterization and scale-up of pegylated nanospheres and nanocapsules for pharmaceutical use. Chem. Eng. Sci. 77, 217–227 (2012).
He, Z. et al. Size-controlled lipid nanoparticle production using turbulent mixing to enhance oral DNA delivery. Acta Biomater. 81, 195–207 (2018).
Shepherd, S. J. et al. Throughput-scalable manufacturing of SARS-CoV-2 mRNA lipid nanoparticle vaccines. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 120, e2303567120 (2023).
Shepherd, S. J. et al. Scalable mRNA and siRNA lipid nanoparticle production using a parallelized microfluidic device. Nano Lett. 21, 5671–5680 (2021).
Hammel, M. et al. Correlating the structure and gene silencing activity of oligonucleotide-loaded lipid nanoparticles using small-angle X-ray scattering. ACS Nano 17, 11454–11465 (2023).
Valencia, P. M., Farokhzad, O. C., Karnik, R. & Langer, R. Microfluidic technologies for accelerating the clinical translation of nanoparticles. Nat. Nanotechnol. 7, 623–629 (2012).
Kroth, I., Karimov, M. & Karongo, R. Automated preparation of oligonucleotide-loaded lipid nanoparticles using Andrew+TM pipetting robot for high-throughput in-vitro screening. Waters https://www.waters.com/content/dam/waters/en/app-notes/2023/720008090/720008090-en.pdf (2024).
Metzger, L. & Kind, M. On the mixing in confined impinging jet mixers — time scale analysis and scale-up using CFD coarse-graining methods. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 109, 464–476 (2016).
Shepherd, S. J., Issadore, D. & Mitchell, M. J. Microfluidic formulation of nanoparticles for biomedical applications. Biomaterials 274, 120826 (2021).
Sreenivasan, K. R. & Antonia, R. A. The phenomenology of small-scale turbulence. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 29, 435–472 (1997).
Feng, J., Markwalter, C. E., Tian, C., Armstrong, M. & Prud’homme, R. K. Translational formulation of nanoparticle therapeutics from laboratory discovery to clinical scale. J. Transl. Med. 17, 200 (2019).
Wilhelm, E., Neumann, C., Duttenhofer, T., Pires, L. & Rapp, B. E. Connecting microfluidic chips using a chemically inert, reversible, multichannel chip-to-world-interface. Lab Chip 13, 4343–4351 (2013).
Ripoll, M. et al. Optimal self-assembly of lipid nanoparticles (LNP) in a ring micromixer. Sci. Rep. 12, 9483 (2022).
Kimura, N. et al. Development of a microfluidic-based post-treatment process for size-controlled lipid nanoparticles and application to siRNA delivery. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 12, 34011–34020 (2020).
Chen, D. et al. Rapid discovery of potent siRNA-containing lipid nanoparticles enabled by controlled microfluidic formulation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 134, 6948–6951 (2012).
Belliveau, N. M. et al. Microfluidic synthesis of highly potent limit-size lipid nanoparticles for in vivo delivery of siRNA. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 1, e37 (2012).
Leung, A. K. K., Tam, Y. Y. C., Chen, S., Hafez, I. M. & Cullis, P. R. Microfluidic mixing: a general method for encapsulating macromolecules in lipid nanoparticle systems. J. Phys. Chem. B 119, 8698–8706 (2015).
Williams, M. S., Longmuir, K. J. & Yager, P. A practical guide to the staggered herringbone mixer. Lab Chip 8, 1121–1129 (2008).
Longwell, S. A. & Fordyce, P. M. micrIO: an open-source autosampler and fraction collector for automated microfluidic input–output. Lab Chip 20, 93–106 (2019).
Hanna, A. R. et al. Automated and parallelized microfluidic generation of large and precisely-defined lipid nanoparticle libraries. Preprint at bioRxiv https://doi.org/10.1101/2025.05.26.656157 (2025).
Nag, K. et al. DoE-derived continuous and robust process for manufacturing of pharmaceutical-grade wide-range LNPs for RNA-vaccine/drug delivery. Sci. Rep. 12, 9394 (2022).
McLeod, E. et al. High-throughput and label-free single nanoparticle sizing based on time-resolved on-chip microscopy. ACS Nano 9, 3265–3273 (2015).
Graewert, M. A. et al. Quantitative size-resolved characterization of mRNA nanoparticles by in-line coupling of asymmetrical-flow field-flow fractionation with small angle X-ray scattering. Sci. Rep. 13, 15764 (2023).
Li, S. et al. Payload distribution and capacity of mRNA lipid nanoparticles. Nat. Commun. 13, 5561 (2022).
Li, S. et al. Single-particle spectroscopic chromatography reveals heterogeneous RNA loading and size correlations in lipid nanoparticles. ACS Nano 18, 15729–15743 (2024).
Penders, J. et al. Single particle automated Raman trapping analysis. Nat. Commun. 9, 4256 (2018).
Lowenthal, M. S., Antonishek, A. S. & Phinney, K. W. Quantification of mRNA in lipid nanoparticles using mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 96, 1214–1222 (2024).
Medina, J. et al. Omic-scale high-throughput quantitative LC–MS/MS approach for circulatory lipid phenotyping in clinical research. Anal. Chem. 95, 3168–3179 (2023).
Kinsey, C. et al. Determination of lipid content and stability in lipid nanoparticles using ultra high-performance liquid chromatography in combination with a corona charged aerosol detector. Electrophoresis 43, 1091–1100 (2022).
Cui, H. et al. LUMI-lab: a foundation model-driven autonomous platform enabling discovery of new ionizable lipid designs for mRNA delivery. Preprint at bioRxiv https://doi.org/10.1101/2025.02.14.638383 (2025).
Maharjan, R., Kim, K. H., Lee, K., Han, H.-K. & Jeong, S. H. Machine learning-driven optimization of mRNA-lipid nanoparticle vaccine quality with XGBoost/Bayesian method and ensemble model approaches. J. Pharm. Anal. 14, 100996 (2024).
Stach, E. et al. Autonomous experimentation systems for materials development: a community perspective. Matter 4, 2702–2726 (2021).
Land, O., Seider, W. D. & Lee, D. Convolutional neural network augmented soft-sensor for autonomous microfluidic production of uniform bubbles. Chem. Eng. J. 499, 156494 (2024).
Szymanski, N. J. et al. An autonomous laboratory for the accelerated synthesis of novel materials. Nature 624, 86–91 (2023).
Chen, J. et al. Navigating phase diagram complexity to guide robotic inorganic materials synthesis. Nat. Synth. 3, 606–614 (2024).
Kusne, A. G. et al. On-the-fly closed-loop materials discovery via Bayesian active learning. Nat. Commun. 11, 5966 (2020).
Jan, E. et al. High-content screening as a universal tool for fingerprinting of cytotoxicity of nanoparticles. ACS Nano 2, 928–938 (2008).
Frei, A. P. et al. Highly multiplexed simultaneous detection of RNAs and proteins in single cells. Nat. Methods 13, 269–275 (2016).
Krohn-Grimberghe, M. et al. Nanoparticle-encapsulated siRNAs for gene silencing in the haematopoietic stem-cell niche. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 4, 1076–1089 (2020).
Connors, J. et al. Lipid nanoparticles (LNP) induce activation and maturation of antigen presenting cells in young and aged individuals. Commun. Biol. 6, 188 (2023).
Haley, R. M. et al. Lipid nanoparticle delivery of small proteins for potent in vivo RAS inhibition. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 15, 21877–21892 (2023).
Han, E. L. et al. Predictive high-throughput platform for dual screening of mRNA lipid nanoparticle blood-brain barrier transfection and crossing. Nano Lett. 24, 1477–1486 (2024).
Liu, R., Jiang, W., Walkey, C. D., Chan, W. C. W. & Cohen, Y. Prediction of nanoparticles-cell association based on corona proteins and physicochemical properties. Nanoscale 7, 9664–9675 (2015).
Alabi, C. A. et al. Multiparametric approach for the evaluation of lipid nanoparticles for siRNA delivery. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 110, 12881–12886 (2013).
Roosa, C. A. et al. Conjugation of IL-33 to microporous annealed particle scaffolds enhances type 2-like immune responses in vitro and in vivo. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 13, 2400249 (2024).
Sahay, G. et al. Efficiency of siRNA delivery by lipid nanoparticles is limited by endocytic recycling. Nat. Biotechnol. 31, 653–658 (2013).
Rui, Y. et al. High-throughput and high-content bioassay enables tuning of polyester nanoparticles for cellular uptake, endosomal escape, and systemic in vivo delivery of mRNA. Sci. Adv. 8, eabk2855 (2022).
Ponsoda, X., Jover, R., Castell, J. V. & Gómez-Lechón, M. J. Measurement of intracellular LDH activity in 96-well cultures: a rapid and automated assay for cytotoxicity studies. J. Tissue Cult. Methods 13, 21–24 (1991).
Marin, D. et al. Safety, efficacy and determinants of response of allogeneic CD19-specific CAR-NK cells in CD19+ B cell tumors: a phase 1/2 trial. Nat. Med. 30, 772–784 (2024).
Dahlman, J. E. et al. Barcoded nanoparticles for high throughput in vivo discovery of targeted therapeutics. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 114, 2060–2065 (2017).
Kim, J., Vaughan, H. J., Zamboni, C. G., Sunshine, J. C. & Green, J. J. High-throughput evaluation of polymeric nanoparticles for tissue-targeted gene expression using barcoded plasmid DNA. J. Control. Release 337, 105–116 (2021).
Guimaraes, P. P. G. et al. Ionizable lipid nanoparticles encapsulating barcoded mRNA for accelerated in vivo delivery screening. J. Control. Release 316, 404–417 (2019).
Rhym, L. H., Manan, R. S., Koller, A., Stephanie, G. & Anderson, D. G. Peptide-encoding mRNA barcodes for the high-throughput in vivo screening of libraries of lipid nanoparticles for mRNA delivery. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 7, 901–910 (2023).
Vaidya, K. et al. Pooled nanoparticle screening using a chemical barcoding approach. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 137, e202420052 (2025).
Boehnke, N. et al. Massively parallel pooled screening reveals genomic determinants of nanoparticle delivery. Science 377, eabm5551 (2022).
El‐Mayta, R. et al. A nanoparticle platform for accelerated in vivo oral delivery screening of nucleic acids. Adv. Ther. 4, 2000111 (2021).
Hatit, M. Z. C. et al. Species-dependent in vivo mRNA delivery and cellular responses to nanoparticles. Nat. Nanotechnol. 17, 310–318 (2022).
Hamilton, A. G. et al. High-throughput in vivo screening identifies differential influences on mRNA lipid nanoparticle immune cell delivery by administration route. ACS Nano 18, 16151–16165 (2024).
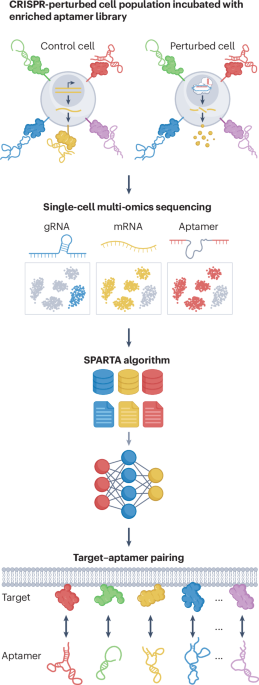
Dobrowolski, C. et al. Nanoparticle single-cell multiomic readouts reveal that cell heterogeneity influences lipid nanoparticle-mediated messenger RNA delivery. Nat. Nanotechnol. 17, 871–879 (2022).
Zhang, Q. et al. Predictable control of RNA lifetime using engineered degradation-tuning RNAs. Nat. Chem. Biol. 17, 828–836 (2021).
Bruchez, M., Moronne, M., Gin, P., Weiss, S. & Alivisatos, A. P. Semiconductor nanocrystals as fluorescent biological labels. Science 281, 2013–2016 (1998).
Paunovska, K. et al. A direct comparison of in vitro and in vivo nucleic acid delivery mediated by hundreds of nanoparticles reveals a weak correlation. Nano Lett. 18, 2148–2157 (2018).
Sago, C. D. et al. High-throughput in vivo screen of functional mRNA delivery identifies nanoparticles for endothelial cell gene editing. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 115, E9944–E9952 (2018).
Buschmann, T. & Bystrykh, L. V. Levenshtein error-correcting barcodes for multiplexed DNA sequencing. BMC Bioinform. 14, 272 (2013).
Witten, J. et al. Artificial intelligence-guided design of lipid nanoparticles for pulmonary gene therapy. Nat. Biotechnol. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41587-024-02490-y (2024).
Cervantes, J., Garcia-Lamont, F., Rodríguez-Mazahua, L. & Lopez, A. A comprehensive survey on support vector machine classification: applications, challenges and trends. Neurocomputing 408, 189–215 (2020).
Yamankurt, G. et al. Exploration of the nanomedicine-design space with high-throughput screening and machine learning. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 3, 318–327 (2019).
Kumar, R. et al. Efficient polymer-mediated delivery of gene-editing ribonucleoprotein payloads through combinatorial design, parallelized experimentation, and machine learning. ACS Nano 14, 17626–17639 (2020).
Pattipeiluhu, R. et al. Anionic lipid nanoparticles preferentially deliver mRNA to the hepatic reticuloendothelial system. Adv. Mater. 34, 2201095 (2022).
Mandl, H. K. et al. Optimizing biodegradable nanoparticle size for tissue-specific delivery. J. Control. Release 314, 92–101 (2019).
Popova, M., Isayev, O. & Tropsha, A. Deep reinforcement learning for de novo drug design. Sci. Adv. 4, eaap7885 (2018).
Tropsha, A., Isayev, O., Varnek, A., Schneider, G. & Cherkasov, A. Integrating QSAR modelling and deep learning in drug discovery: the emergence of deep QSAR. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 23, 141–155 (2024).
Walsh, D. J. et al. Community Resource for Innovation in Polymer Technology (CRIPT): a scalable polymer material data structure. ACS Cent. Sci. 9, 330–338 (2023).
Kuenneth, C. & Ramprasad, R. polyBERT: a chemical language model to enable fully machine-driven ultrafast polymer informatics. Nat. Commun. 14, 4099 (2023).
Meyer, T. A., Ramirez, C., Tamasi, M. J. & Gormley, A. J. A user’s guide to machine learning for polymeric biomaterials. ACS Polym. Au 3, 141–157 (2023).
Xue, K. et al. Biomaterials by design: harnessing data for future development. Mater. Today Bio 12, 100165 (2021).
Haley, R. M. et al. Lipid nanoparticles for in vivo lung delivery of CRISPR-Cas9 ribonucleoproteins allow gene editing of clinical targets. ACS Nano 19, 13790–13804 (2025).
Tang, C. et al. mRNA-laden lipid-nanoparticle-enabled in situ CAR-macrophage engineering for the eradication of multidrug-resistant bacteria in a sepsis mouse model. ACS Nano 18, 2261–2278 (2024).