- News & Views
- Published:
Nanomedicine
Subjects
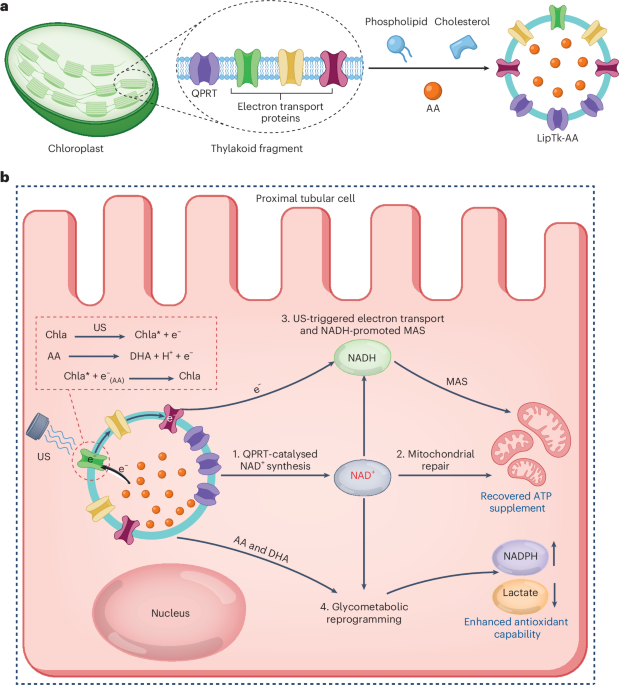
Ultrasound-responsive lipid nanoparticles encapsulating thylakoid fragments sourced from plants and ascorbic acid restore mitochondrial function, treating acute kidney injury in mice and pigs.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
$32.99 / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $9.92 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

References
-
Bhargava, P. & Schnellmann, R. G. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 13, 629–646 (2017).
-
Kellum, J. A. et al. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 7, 52 (2021).
-
van der Rijt, S., Leemans, J. C., Florquin, S., Houtkooper, R. H. & Tammaro, A. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 18, 588–603 (2022).
-
Li, L. et al. Exploration 3, 20220148 (2023).
-
Jiang, D. et al. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2, 865–877 (2018).
-
Hou, J. et al. Nano Lett. 20, 1447–1454 (2020).
-
Sun, T. et al. Adv. Funct. Mater. 29, 1904833 (2019).
-
Hershberger, K. A., Martin, A. S. & Hirschey, M. D. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 13, 213–225 (2017).
-
Lei, Y. et al. Nat. Biomed. Eng. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41551-025-01402-y (2025).
-
Wang, Y., Li, S., Liu, L., Lv, F. & Wang, S. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 56, 5308–5311 (2017).
-
Katoh, A., Uenohara, K., Akita, M. & Hashimoto, T. Plant Physiol. 141, 851–857 (2006).
-
Li, Y. et al. ACS Nano 12, 1455–1461 (2018).
-
Zhou, H.-L. et al. Nature 565, 96–100 (2019).
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
W.C. declares competing interests with the following corporations: Portrai, Inc., rTR Technovaation Corporation and Four Health Global Pharmaceuticals, Inc. The other authors declare no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hsu, J.C., Zhou, J. & Cai, W. Metabolic reprogramming with ultrasound-responsive nanovesicles. Nat. Biomed. Eng (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41551-025-01460-2
-
Published:
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41551-025-01460-2